How I’d Set Up Safe and Fast Deployments with Azure DevOps and GitHub Advanced Security
Deploying to production can be fast, fun, and totally low-stress! Here’s exactly how I’d set up Azure DevOps with GitHub Advanced Security for safe and reliable .NET application deployment. We'll use pull requests, branch policies, robust pipelines, approval gates, and Azure App Service deployment slots to keep things smooth and secure. Let’s dive in!
Step 1: Kick Off with Pull Requests and Branch Policies 🎉
First up: Pull Requests (PRs). PRs aren’t just a formality; they’re where team collaboration happens and code quality is guaranteed! If I’m setting this up, here’s what my PR game would look like:
Pull Requests: Let’s Get Collaborating!
- Enable PR Workflow: Head over to Repos > Pull Requests in Azure DevOps and enable a PR workflow. Every code change should go through a PR—it’s where team feedback lives!
- Trigger Builds and Tests Automatically: Set up Azure DevOps to run builds and tests on every PR so that we catch issues long before code reaches production.
trigger:
branches:
include:
- main
pr:
branches:
include:
- main
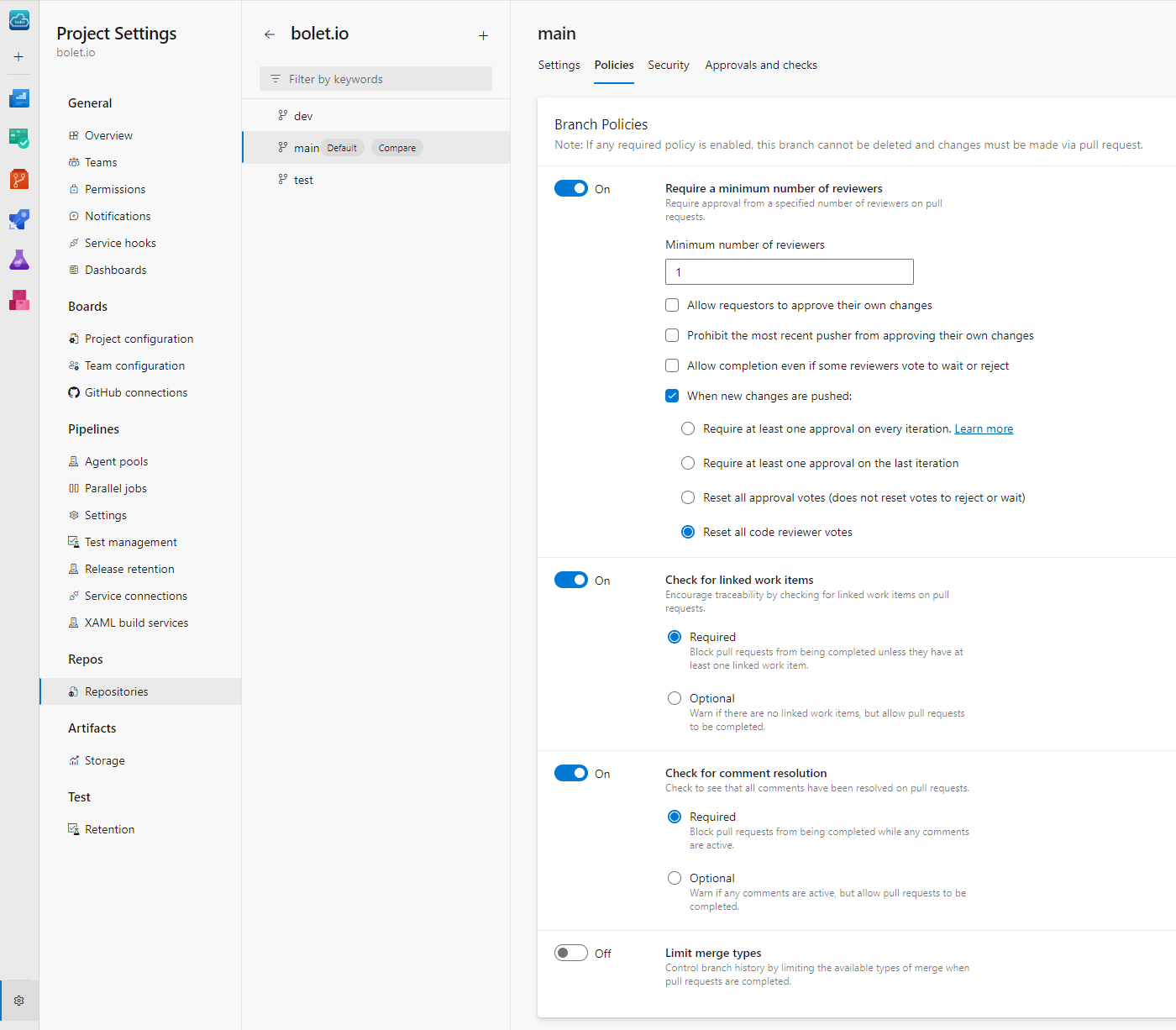
Setting Up Branch Policies: Your Quality Control 🛡️
Branch policies make sure only high-quality code gets merged. Here’s how I’d set it up:
- Navigate to Branch Policies: In Repos > Branches, find your main branch, click the three-dot menu, and select Branch policies.
- Define Your Rules:
- Require Reviewers: Set it so that at least one teammate has to review each PR.
- Automated Build Validation: Link your build pipeline here to make sure code doesn’t merge unless it passes all checks.
- Link Work Items: Require a work item with every PR. This makes it crystal clear what’s being delivered and why.
- Limit Merge Types: Set it to squash merge only to keep the history clean.
Step 2: Level Up Security with GitHub Advanced Security 🔒
With PRs and branch policies locking down code quality, it’s time to bring in GitHub Advanced Security to catch any security hiccups. Here’s what I’d add to keep things secure:
Configuring GitHub Advanced Security
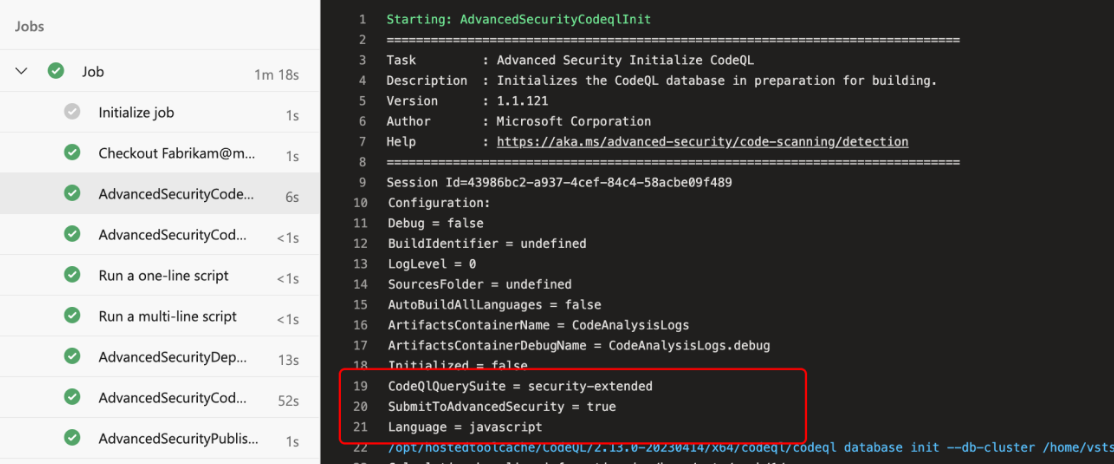
- Enable Code Scanning with CodeQL: Use CodeQL to check code for security issues—think of it as having a security guard for every PR. In GitHub, head to the Security tab, select Code scanning alerts, and configure CodeQL:
jobs:
analyze:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Initialize CodeQL
uses: github/codeql-action/init@v1
with:
languages: dotnet
- name: Perform CodeQL Analysis
uses: github/codeql-action/analyze@v1
- Enable Secret Scanning: Protect against accidental key leaks by enabling Secret Scanning in Settings. GitHub flags any checked-in secrets before they go anywhere dangerous.
- Set Up Dependency Alerts: Enable Dependency Review in the Security tab to track any insecure third-party libraries.
Step 3: Build a Robust .NET Pipeline in Azure DevOps 🔄
Next up, let’s build a pipeline that automates build, test, and deployment steps for smooth releases. Here’s how I’d do it for a .NET project:
Setting Up the Pipeline YAML File
-
Create a New Pipeline: In Azure DevOps, go to Pipelines, select Create Pipeline, and link it to your repo.
-
Define the Stages:
Build Stage: This stage compiles your code and checks for issues:
stages:
- stage: Build
jobs:
- job: BuildJob
pool:
vmImage: 'windows-latest'
steps:
- task: UseDotNet@2
inputs:
packageType: 'sdk'
version: '6.x'
- task: DotNetCoreCLI@2
inputs:
command: 'restore'
projects: '**/*.csproj'
- task: DotNetCoreCLI@2
inputs:
command: 'build'
projects: '**/*.csproj'
arguments: '--configuration Release'
Test Stage: Run automated tests to ensure everything’s working.
- stage: Test
jobs:
- job: TestJob
pool:
vmImage: 'windows-latest'
steps:
- task: DotNetCoreCLI@2
inputs:
command: 'test'
projects: '**/*.csproj'
arguments: '--configuration Release --no-build'
Deploy Stage: Push the tested code to staging or production.
- stage: Deploy
jobs:
- deployment: DeployJob
environment: 'staging'
pool:
vmImage: 'windows-latest'
steps:
- task: DotNetCoreCLI@2
inputs:
command: 'publish'
projects: '**/*.csproj'
arguments: '--configuration Release --output $(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)'
- task: CopyFiles@2
inputs:
SourceFolder: '$(Build.ArtifactStagingDirectory)'
TargetFolder: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/drop'
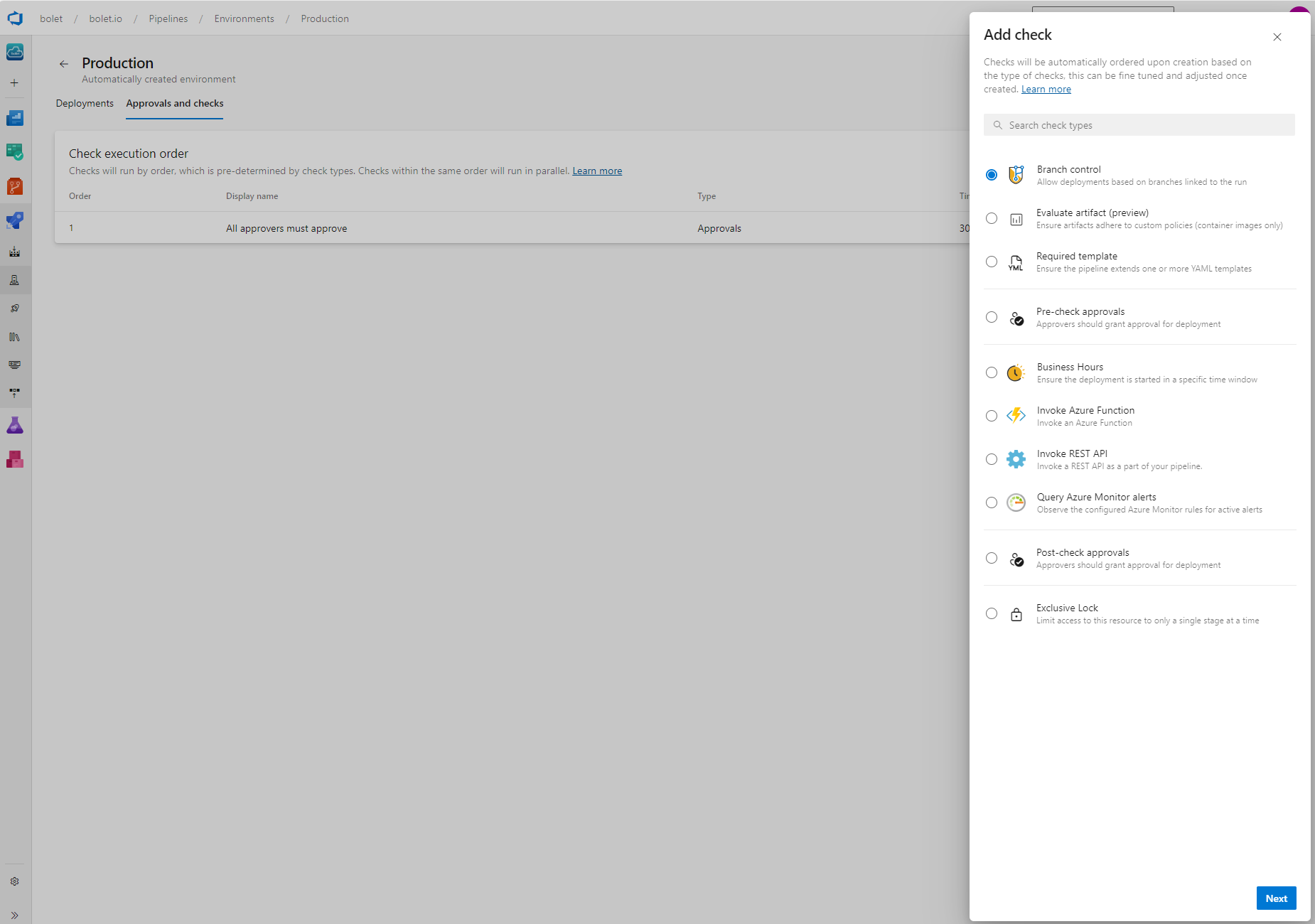
Step 4: Environments and Approval Gates as Your Final Quality Check ✅
Environments and approval gates add a final “Are we sure?” step before production.
- Define Environments: Go to Pipelines > Environments and add Dev, Staging, and Production environments. Customize each with environment-specific settings.
- Set Up Approval Gates: Add an approval gate to the production environment. This stops the pipeline until someone on the team reviews and approves it.
Step 5: Use Deployment Slots for Smooth Production Rollouts 🎭
Deployment slots in Azure App Service allow you to test in a production-like environment before going live. Here’s how I’d set them up:
- Create a Staging Slot: In Azure App Service, go to Deployment slots and add a slot named “staging.” This slot mirrors production, so you can test in a real-world setup without affecting live users.
- Deploy to Staging Slot: Modify your pipeline YAML to deploy to staging first:
- stage: DeployToStaging
jobs:
- deployment: DeployToStagingJob
environment: 'staging-slot'
pool:
vmImage: 'windows-latest'
steps:
- task: AzureWebApp@1
inputs:
azureSubscription: '<YourAzureSubscription>'
appType: 'webApp'
appName: '<YourAppName>'
deployToSlotOrASE: true
resourceGroupName: '<YourResourceGroup>'
slotName: 'staging'
package: '$(System.DefaultWorkingDirectory)/drop'
- Swap Slots to Go Live: Once verified in staging, swap slots to make the new version live with minimal downtime:
- stage: SwapSlots
jobs:
- job: SwapJob
steps:
- script: az webapp deployment slot swap --name <YourAppName> --slot staging --resource-group <YourResourceGroup>
displayName: 'Swap Staging to Production'
Monitor Production: If anything looks off, just swap slots back for a quick rollback.
Wrapping Up 🎉
Following these steps, you’ll have a streamlined Azure DevOps setup that makes deployments safe, fast, and repeatable. By using PRs, branch policies, GitHub Advanced Security, automated pipelines, approval gates, and deployment slots, you can deliver value to users without sacrificing quality or risking downtime.
This pipeline setup combines the speed of automation with the security of human approvals, making it perfect for fast, reliable, and secure production releases. Happy deploying!